Over the years, I’ve seen many students struggle with the past simple and past continuous tenses. I completely understand—at first glance, they both seem to refer to actions in the past, so it’s easy to mix them up. However, once you understand the purpose of each tense and when to use them, it becomes much simpler. In this lesson, I’ll explain the differences, provide examples, and include practice exercises to help you master these tenses.
Past Simple
Past Simple
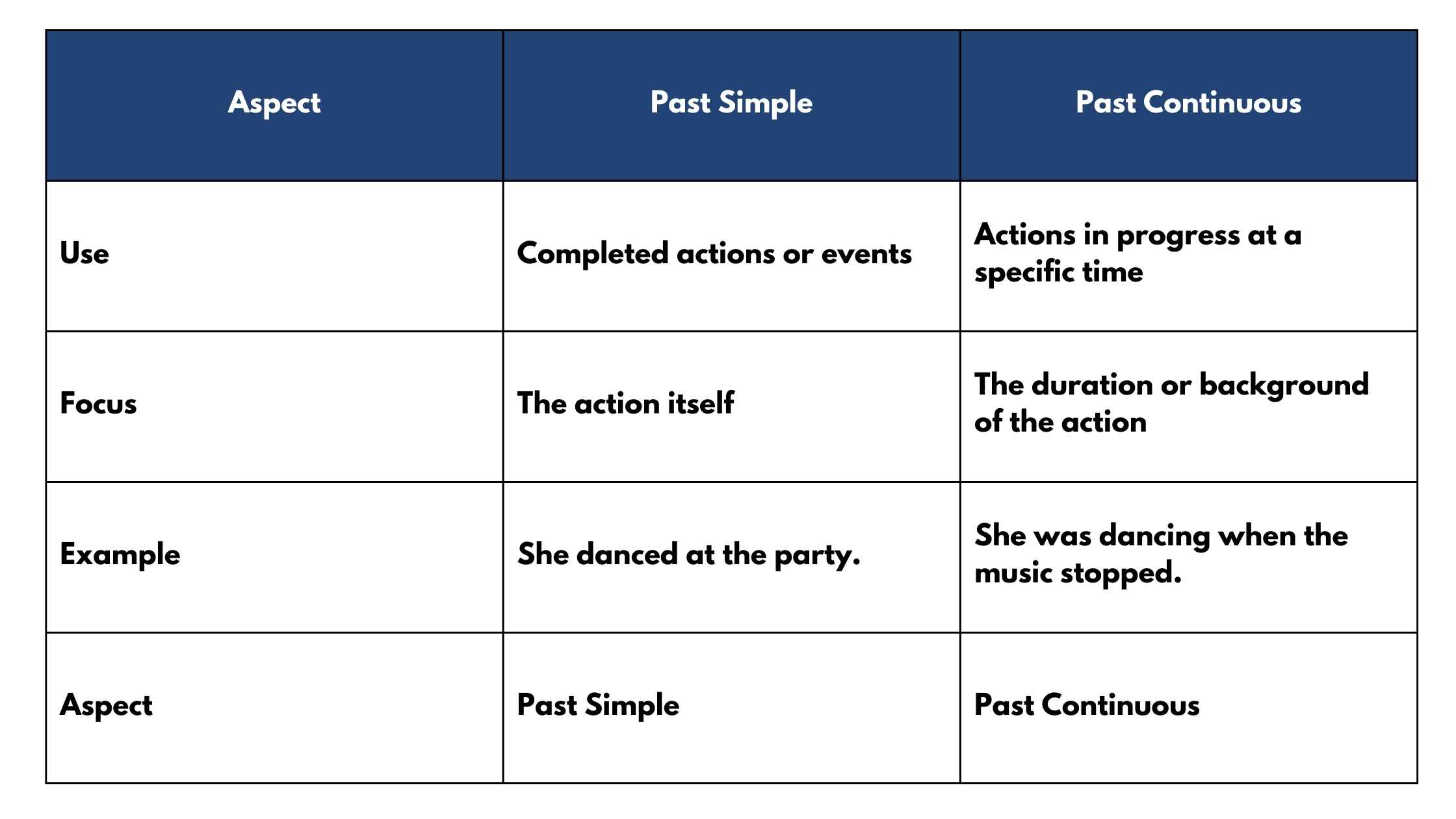
The past simple tense is used to describe completed actions or events that happened at a specific time in the past. It’s your go-to tense when you want to talk about something that’s finished.
When to Use the Past Simple
Completed Actions in the Past
"I visited Paris last summer."
"She finished her homework yesterday."
A Series of Completed Events
"He woke up, brushed his teeth, and left for work."
"They arrived, unpacked, and went to the beach."
General Facts About the Past
"The Titanic sank in 1912."
"He was born in 1990."
Structure of Past Simple
For regular verbs: base verb + -ed (e.g., "I walked").
For irregular verbs: Use the specific past tense form (e.g., "I went," "She saw").
Negative: Use did not (didn’t) + base verb (e.g., "I didn’t walk").
Question: Start with did + subject + base verb (e.g., "Did they walk?").
Past Continuous
Past Continuous
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive, is used to describe actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. It’s often used to set the scene or talk about actions that were interrupted.
When to Use the Past Continuous
Actions in Progress at a Specific Time
"I was reading a book at 8 p.m. last night."
"She was cooking dinner when I called."
Background Descriptions
"The sun was setting, and the birds were singing."
"He was walking through the park when he met her."
Interrupted Actions
"I was watching TV when the power went out."
"They were playing football when it started to rain."
Two Simultaneous Actions
"She was reading while he was writing."
"We were chatting as they were preparing the presentation."
Structure of Past Continuous
Subject + was/were + verb + -ing (e.g., "I was walking," "They were singing").
Negative: Add not (e.g., "I was not walking," "They were not singing").
Question: Start with was/were (e.g., "Was she walking?" "Were they singing?").
📚 Join The Basics of English Course! 🚀